Our view at Stack - Shopify has just about everything you need if you're looking to sell online. It excels with unlimited products, user-friendly setup, and 24/7 support. It offers 6,000+ app integrations, abandoned cart recovery, and shipping discounts up to 88%. Plus, it allows selling both online and in-person, scaling as your business grows.
Solvency, just like profitability, is a financial metric every business owner should be familiar with.
Financial solvency is required for long-term survival. If a business is insolvent, it can find itself filing for bankruptcy and going out of business.
To keep your ecommerce business financially sound, learn what solvency means, how it works, and some practical strategies your business can use to improve its financial solvency.
What is solvency in simple terms?
Solvency is a financial metric that evaluates a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations. In business, debt is often a double-edged sword. While it can be an exceptional financial catalyst, it can also lead to a business’s downfall if poorly managed.
But solvency is sometimes confused with liquidity. While the two are similar, they are not the same.
Liquidity vs. solvency
Liquidity measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial obligations. Solvency measures a business’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations.
A liquidity problem occurs when a company cannot pay its short-term liabilities, like employee wages or supplier invoices, using cash on hand and outstanding customer receivables. Liquidity can easily become a concern for an ecommerce company.
For example, assume a company makes large inventory purchases in Q1 to prepare for a busy summer selling season. The company may face liquidity issues in Q2 because a large chunk of its cash is tied up in inventory that won’t sell for several months. This leaves little cash coming in to cover ongoing expenses like rent, wages, or order fulfillment.
On the flip side, a business experiences a solvency problem when it can’t pay its long-term liabilities, like loans and mortgages, even if it sells all of its assets.
When the total of a company’s current assets (e.g., cash, inventory, receivables, equipment, etc.) is less than its total liabilities, the business has a solvency problem. While a liquidity issue can be frustrating and can slow down operations, a solvency problem can be dire.
Here’s how to visualize the difference between liquidity and solvency.
| Liquidity | Solvency | |
|---|---|---|
| Time span | Within one year | Long-term financial outlook |
| Ability measured | To pay current financial obligations | To meet current and future financial obligations |
| Assets considered | Assets that can easily convert to cash | Total assets |
| Liabilities considered | Debts due within one year | All debts |
| Impact | Short-term cash flow problems | Potential bankruptcy |
| Example | Company with high inventory but low sales | Company with high debt and declining sales |
How does solvency work?
Because solvency is a key financial benchmark, merchants need to know if their businesses are solvent. But how?
The easiest way to determine if a business is solvent is to sum up its total assets and total liabilities and then subtract its total liabilities from its total assets. To calculate solvency, use this formula:
Solvency = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
For instance, suppose an ecommerce store’s assets include:
| Ecommerce Shop Assets | Dollar Value |
|---|---|
| Cash | $300,000 |
| Inventory | $450,000 |
| Software | $200,000 |
| Total assets | $950,000 |
And assume its liabilities are:
| Ecommerce Shop Liabilities | Dollar Value |
|---|---|
| Vendor/supplier invoices | $100,000 |
| 10-year bank loan | $500,000 |
| Total liabilities | $600,000 |
Since the company’s assets exceed liabilities by $350,000, this company is solvent since it has an extra $350,000 to cover its total liabilities.
It also helps for business owners to understand these three solvency ratios.
Debt-to-equity ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio measures how a company finances itself with debt (loans and payables) compared to its own money (equity). It reflects the company’s leverage. In this calculation, debt is the numerator and equity is the denominator. To calculate debt-to-equity, use this formula:
Debt to Equity = Total Debt ÷ Total Equity
A higher ratio, typically over 2, should be a concern to an ecommerce entrepreneur. A debt-to-equity ratio of 2 means that for every $1 of equity, there is $2 of debt. This is when you can creep into solvency issues.
The ideal debt-to-equity ratio varies widely by industry. For example, businesses in capital-intensive industries, such as airlines, have higher debt-to-equity ratios. But technology and healthcare companies have lower debt-to-equity ratios.
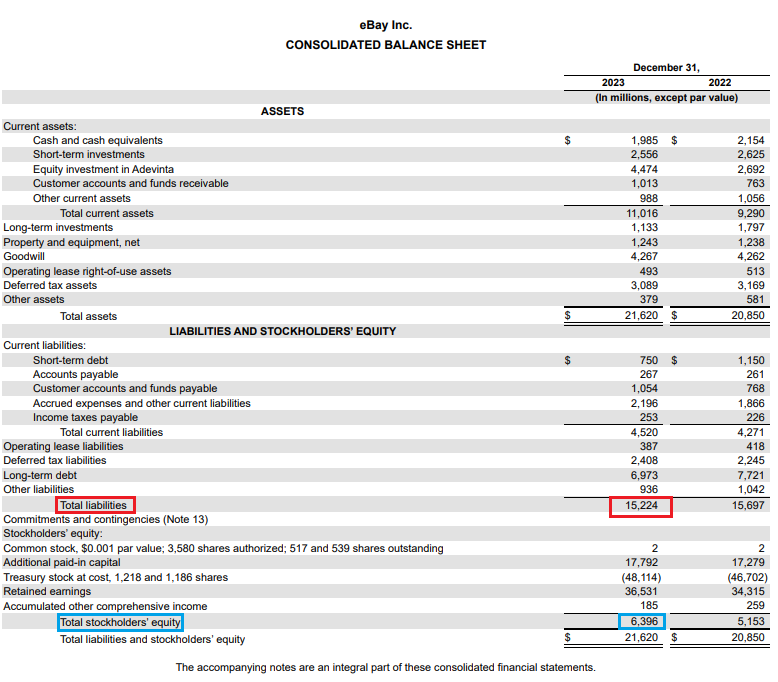
Let’s look at an example from popular ecommerce company eBay’s December 31, 2023 balance sheet.
Ignore all the words and numbers. Only look at the items blocked in red and blue. These are the two numbers needed to calculate eBay’s debt-to-equity ratio.
As of December 31, 2023, eBay had a debt-to-equity ratio of 2.38 ($15,224 ÷ $6,396). As an established ecommerce company, this ratio wouldn’t raise solvency concerns. But for newer ecommerce businesses, this would warrant ongoing monitoring.
Interest coverage ratio
Another way to know if your business is solvent is to calculate its interest coverage ratio.
The interest coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its interest expense on its debt. It tells you how easily the company’s current earnings can cover the interest expense; hence the term “Interest Coverage.”
You can calculate your interest coverage ratio by dividing your company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expense. Use this formula to calculate interest coverage ratio:
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT ÷ Interest Expense
EBIT shows you how much profit your business made from its core operations before considering extra expenses like income taxes and interest.
A low-interest coverage ratio suggests a company may have difficulty paying its interest expense. But a higher ratio means the business has more wiggle room to pay its debt obligations.
What interest coverage ratio should ecommerce businesses aim for? A company with consistent revenues should aim for a minimum interest coverage ratio of 2.
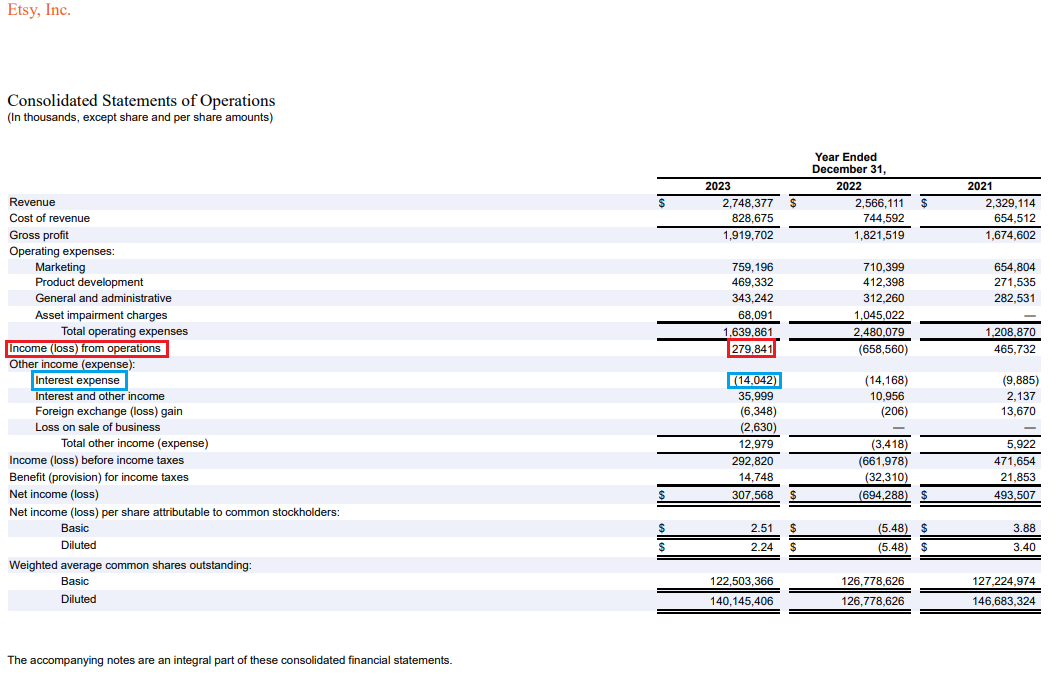
Let’s look at another real-world example from the ecommerce brand Etsy. Again, ignore all the words and numbers. Only look at the items blocked in red and blue. These are the two numbers needed to calculate eBay’s interest coverage ratio.
As of December 31, 2023, Etsy’s interest coverage ratio was a solid 19.9 ($279,841 ÷ $14,042). This is a strong financial position because it means that for approximately every $20 Etsy makes, it spends only $1 on interest.
Equity ratio
Another financial metric you use to evaluate your company’s solvency is the equity ratio.
Business owners and analysts can evaluate a company’s solvency by analyzing its debt using the debt-to-equity ratio or the interest coverage ratio. But you can also evaluate a company’s solvency by reviewing its equity level.
Equity is how much of your business you own after deducting what the company owes to others. The idea behind the equity ratio is that if equity is high, then debt will correspondingly be low. The formula for the equity ratio is total equity ÷ total assets.
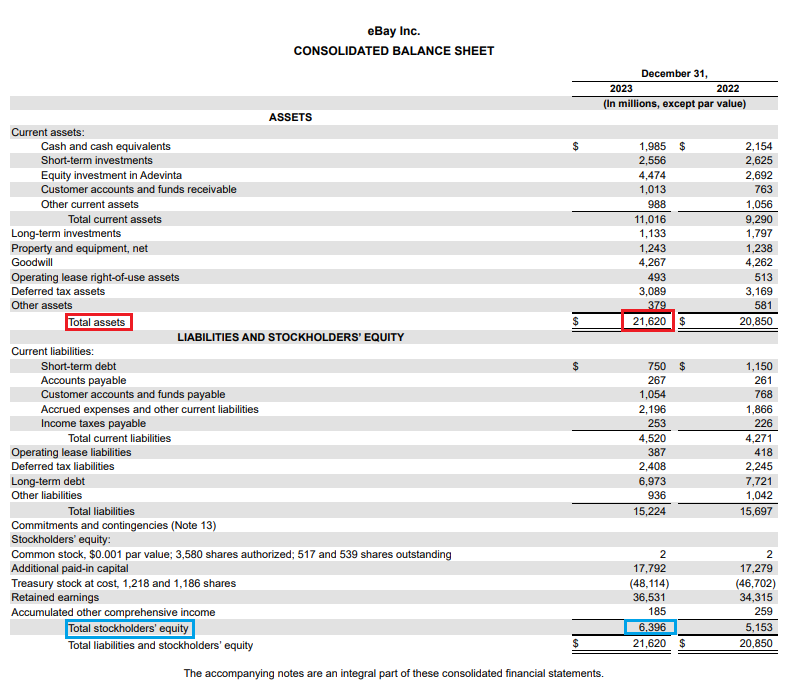
Let’s go back and look at eBay’s balance sheet and calculate its equity ratio. Remember to only look at the items blocked in red and blue. These are the two numbers needed to calculate eBay’s equity ratio.
As of December 31, 2023, eBay’s equity ratio was 0.295 ($6,396 ÷ $21,620).
An equity ratio below 1.0 is worthy of attention because it means the company has more debt than equity. While this might not be a problem, it’s worth monitoring.
Factors influencing a company’s solvency
Monitoring your company’s solvency helps ensure its long-term survival and provides peace of mind to you as a business owner.
Factors that affect solvency can be broken down into three categories:
- Financial management
- Market factors
- Operational issues
Financial management
Poor financial management can lead to insolvency, and inefficient inventory management can drain cash flow. Overstocking slow-moving products ties up working capital, but understocking can lead to lost sales.
Keeping a close watch over sales trends, including seasonality and customer purchasing patterns, can help with under or overstocking. Solvency can be traced back to profitability. A company consistently generating healthy profits has a greater ability to meet debt obligations and remain solvent.
Market factors
Economic conditions beyond your control can lead to solvency problems. For example, the government can change its tax regime, import or export policy, or regulatory requirements.
Staying ahead of the competition, identifying changes in customer preferences, or recognizing industry trends can help your business stand out and attract new customers and increase sales.
Operational issues
Your ecommerce company’s operations are the backbone of your business. Slow order fulfillment and unreliable shipping can damage brand loyalty and lead to lost sales and reduced cash flow.
Ensure your marketing campaigns are designed effectively. A poorly designed campaign that cannot generate a good return on investment can eat into cash flow. Rapid expansion of product lines or entering a new category space that is not well thought out can also quickly deplete cash.
Other factors that can affect solvency include technological changes, natural disasters, and poor leadership.
Strategies for improving solvency
Solvency is often a life-or-death issue for a business. That means scrutinizing your solvency metrics can be life-saving.
If you’re worried about solvency and want to shore it up a bit, consider the following strategies.
Improve your profits
There are two ways you can increase your profits: increase sales or reduce costs. Typically, you will start by reducing costs because it’s the easiest and can give you results in days.
Consider negotiating better prices with suppliers and shipping vendors. But don’t overlook the need to increase sales. Cutting costs can only do so much to improve a company’s financial health. Consider dynamic pricing models where prices adjust based on demand, competition, and customer behavior.
Restructure your debts
Before risking default, consider restructuring your debts.
Restructuring debts that lead to lower interest rates or extended repayment schedules can give business owners breathing room as they figure out how to put their business operations on a more sustainable track.
Manage inventory efficiently
Review your inventory management techniques to avoid over- and under-stocking. If you haven’t already, create procedures to prevent product damage to reduce waste and shrinkage. Ensure you are completing regular inventory audits to identify any issues with inventory storage.
Securing your future as a business owner
While you should know whether your company is earning profits, you should also assess whether it will continue to make profits for the foreseeable future. That’s why solvency, which measures whether a business can meet its long-term financial obligations, is crucial.
The debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and equity ratio can help entrepreneurs evaluate whether their companies are solvent or not.
And if you find your solvency metrics aren’t stellar, you may want to explore restructuring your debts and cutting unnecessary costs.
Solvency FAQ
What is solvency in finance?
Is solvency a good thing?
What is an example of solvency?
Are solvency ratios the same for every company?
If Shopify is of interest and you'd like more information, please do make contact or take a look in more detail here.
Credit: Original article published here.
