In today’s digital age, the way we learn and train has been transformed by technology, and at the heart of this transformation is Learning Management Systems (LMSs). An LMS is a versatile tool that helps educators, trainers, and organizations manage and deliver educational content efficiently.
From schools and universities to corporate training programs and government agencies, the use of LMS platforms has revolutionized the approach to teaching and learning. The demand for online and blended learning is growing rapidly, as is the size of the LMS market, which is expected to reach 69.6 billion by 2030.
Because of this, understanding the role and benefits of an LMS becomes essential, especially for educators and online instructors. This article explains what an LMS is, its benefits and different types, and how you can choose the right one for your business!
P.S. If you are looking for an LMS, check out our list of the best Learning Management Systems in the market.
Your professional looking Academy in a few clicks
Start FREE Trial
What is a Learning Management System (LMS)?
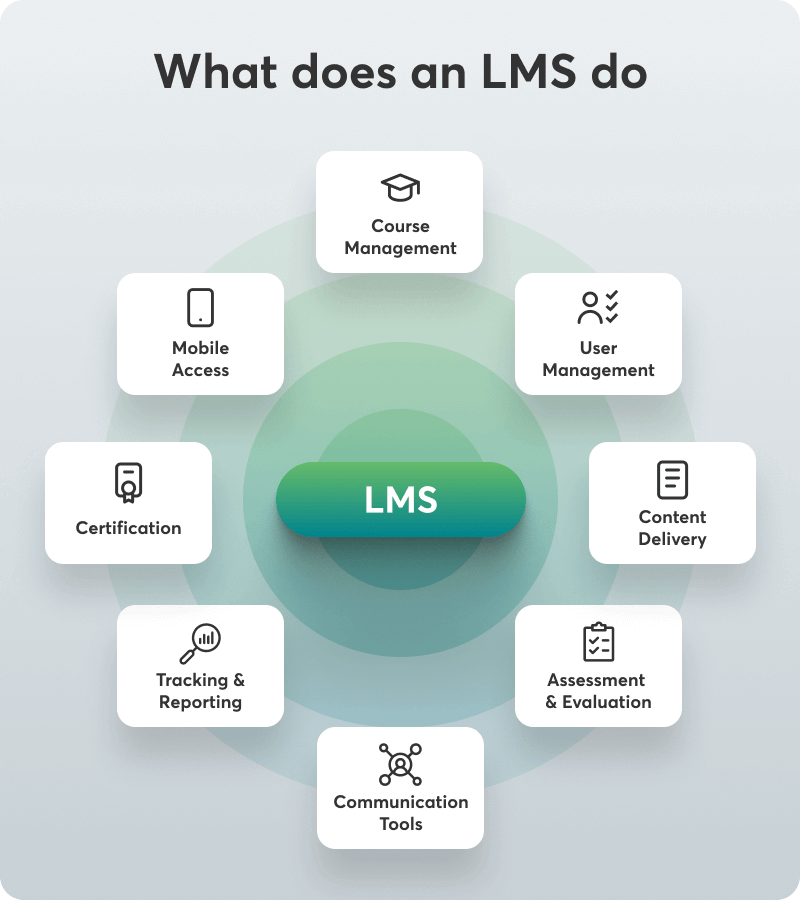
An LMS is a tool that facilitates the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, and delivery of educational courses or training programs. It is used widely in the eLearning industry and is a great management and distribution vehicle for learning programs across various sectors.
LMSs support synchronous (live) and asynchronous (self-paced) learning, providing tools for creating interactive content, conducting assessments, and monitoring learner progress. This technology has become essential in modern education and training, enabling efficient and effective learning experiences tailored to the needs of diverse users.
Use cases of learning management systems
The role and functions of LMS software vary depending on the learning goals of the instructor or company that is using it, and ultimately the industry they are in.
These are the most common categories of individuals and organizations that utilize an LMS:
Schools / Academic Institutions
A school or any other academic or learning institution uses an LMS to help teaching professionals assign online learning, share educational resources and materials (assessments, ebooks, quizzes), and manage student grades.
In many cases, it aids the education management of a K-12 school, as it can monitor student enrollments, keep records up-to-date, store students’ information, including their contact details, and track learner progress.
Note
Virtual and Elearning-based Learning Associations
Online institutions such as LinkedIn Learning, Udemy, and Khan Academy allow people to grow their skills through online courses and professional development programs. These are not considered free LMSs but learning marketplaces.
Corporate Training Departments
Small businesses, medium-sized companies, and large enterprises that want to offer employees an easily accessible and standardized learning environment as a training solution where they learn and grow at their own pace purchase LMSs.
A Corporate Learning Management System (LMS) can streamline the training management process, helping you build an online corporate training program that covers your training needs. It can also make the onboarding process for new employees a lot easier.
Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations often don’t have the appropriate resources to train volunteers effectively. Using an LMS as a training platform can help standardize the training process and make it available and accessible to all internal stakeholders.
Nonprofits also leverage LMS systems to sell online courses as an additional revenue source to support their mission.
Content Providers
Content providers create training content, promote it, and sell it. With the right LMS that offers multiple monetization options, any course instructor can create, manage, and sell educational content to those interested in boosting their knowledge or skills in any field.
Wholesale Companies
An LMS can keep distributors, resellers, and internal sales teams up-to-date with the latest products and promotions. It also enables collaborative learning among internal (existing employees or new hires) and external stakeholders (learners) through tutorials, webinars, and other collaboration tools and interactive learning activities.
Why use a learning management system?
With an LMS, you can plan, manage, and deliver training content for different purposes depending on who you are or who you represent. You can also use it to track online training initiatives.
These purposes may serve different functions in any of these settings:
Educational institutions: An LMS offers an open, user-friendly, and flexible learning environment that creates personalized learning paths for students, delivers online course modules, and even supplements real-time in-class instruction. This works as part of a blended learning setting where face-to-face instruction is still offered at schools, colleges, and universities.
Corporate training: HR resources administration initiatives in an organization use an LMS as a training tool. It can be part of talent management or the onboarding process, employee training, partner training, member training, compliance training, and sometimes sales enablement. The most prominent industries include healthcare/medicine, sales/marketing, software, and tech.
Customer training: Some companies want to educate customers on how to use their products in addition to educating their staff. These companies use an LMS to allow their customers to learn about their product or service—what they sell and how it works. This reduces support calls and increases engagement and product satisfaction.
Extended enterprise training: Similar to what they do for their customers, companies offer online training resources to external sales channels, partners, and franchisees.
Freelancing: LMSs are also used by people who want to monetize knowledge. They create and sell online courses by teaching what they know, establishing a viable or additional source of income as freelance online instructors. These guys or gals are also known as edupreneurs.
As you can see, an LMS can carry out all of these activities and be used in different ways to achieve a unique outcome. It sounds like the ultimate multi-tool!
The benefits of using an LMS
Using an LMS has its advantages, but this depends much on the features it offers. Every LMS is different because of what it can do for you.
According to the Encyclopedia of Distributed Learning, the six elements that make up the LMS concept are interoperability, accessibility, reusability, durability, maintenance ability, and adaptability.
So, generally, every LMS can:
Diving into more specifics, though, it can do all of the following for learners, businesses, and schools:
LMS benefits for learners
LMS benefits for businesses
LMS benefits for schools/educational institutions
What are the different types of LMSs?
Even though an LMS can do many great things, not every LMS can do everything. There are many categories of LMSs because each specializes in certain aspect(s) or seems to serve a specific purpose better than others.
LMSs differ in terms of:
The following table gives you a quick overview of the different types of LMSs available.
Certainly! Here’s the table with the provided data, formatted according to your template:
But let’s explore these in more detail.
Deployment type
Open Source: An open-source learning management system (aka open source LMS) is the free version of an LMS in which the source code is open and free for anyone to use and adapt to their specifications.
Commercial:
Desktop Application: This is an LMS that works as a desktop application. Some desktop apps also work on smart devices, which can facilitate team collaboration, but not every LMS offers this option.
Mobile Application: An LMS that is accessible on smartphone devices and you can upload learning content while on the go.
Custom-built: A custom-built LMS is a tailor-made system built and maintained by a team of developers employed or contracted by your company.
Industry-specific: An LMS developed for a specific industry hosts training assets such as certifications, training activities, or games related to industry-specific skills and knowledge.
Pricing model
Pay per active user: you pay for each active user during each payment circle.
Pay per learner: you pay for the number of learners regardless of their online/offline status.
Pay as you go: you pay for what you use – the number of users and what courses they take.
License fee/subscription: you pay a monthly or yearly license fee to use the system.
Licensing
Free License: Free license LMS is usually an open-source system. Although this is a free LMS, it has an added expense, which goes directly to the programmer or the IT team you hire to work the code and any additional plugins for you.
Paid License: Paid LMSs require a monthly or yearly fee to use. While most systems work on subscription (recurring payments), some may offer the option to buy it upfront with a one-time payment.
Specification
Not every LMS supports the same elearning formats. To keep up with portability and the eLearning standards, some LMSs support one (or more) of the following formats:
These formats allow you to import the same content into a different standards-compliant LMS. For an LMS to stay current in the market, it needs to be able to support any of these eLearning standards. Looking out for these when investing in an LMS vendor is important.
Customer type
An LMS may differ in terms of its target audience too. So it may specifically be for Enterprise training – targeting enterprises and other organizations (Partner LMS/Enterprise LMS), Corporate training – targeting businesses and corporations (Corporate LMS), or Academic education– targeting educational institutions or schools (Academic LMS).
Key Differences Between LMS vs. LCMS, LXP, and LRS
Educational technology, as we know it today, also features a variety of platforms designed to support different aspects of learning and content management.
So, apart from the LMS, you might have also read or heard about:
The table below lists the key differences between these systems and explains each’s purpose, primary focus, users, and key features.
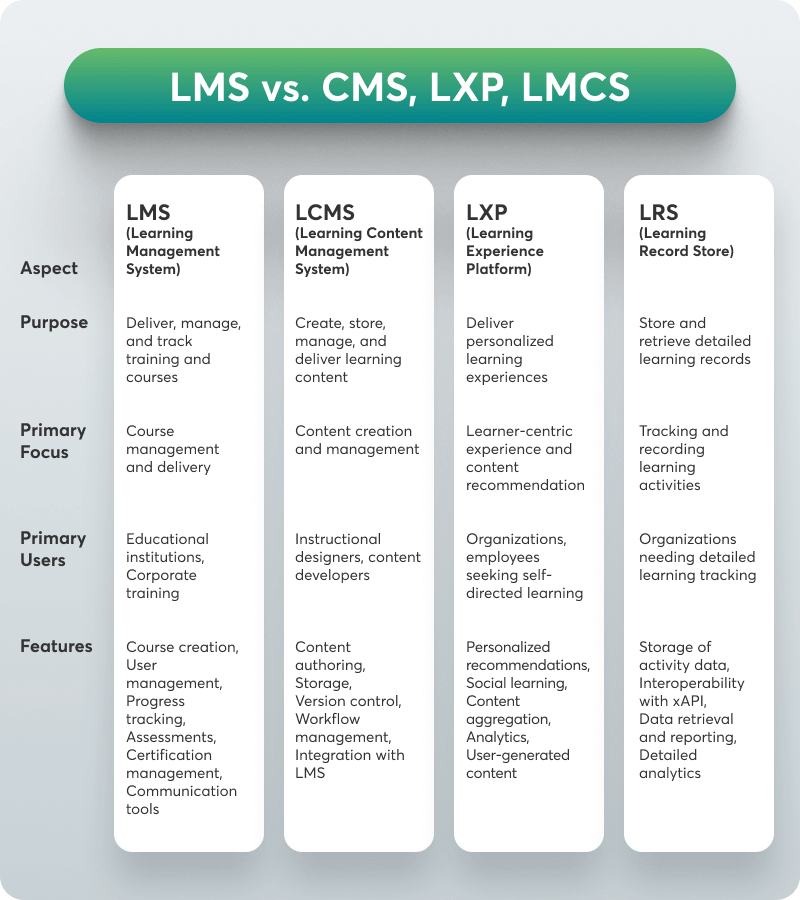
LCMS (Learning Content Management System)
An LCMS focuses on creating, storing, managing, and delivering learning content. It is a web-based portal that enables instructional designers and content creators to develop, reuse, and manage learning materials more efficiently in a collaborative environment.
LXP (Learning Experience Platform)
An LXP is a learner-centric platform that focuses on delivering personalized learning experiences. It aggregates content from multiple sources and uses AI to recommend learning paths and resources tailored to individual learners.
LRS (Learning Record Store)
An LRS is a specialized database designed to store and retrieve learning records. It works with the Experience API (xAPI) to track and record learning activities across multiple platforms and contexts.
Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the right learning management tool for your business or organization.
How do learning management systems work?
Every LMS is different and packed with unique capabilities.
Some LMS platforms offer built-in course authoring tools that help you produce training content. In contrast, others don’t and can only assist you in other aspects, like managing and distributing training materials.
Using an LMS, you can upload these training materials – also known as ‘training assets’ to the learning base of the system. In this online learning environment that you create, remote learners can access your course content from their desktop or mobile devices.
The Essential LMS Features
LMSs have advanced and expanded their toolkit in ways that were impossible a decade ago. Today, an LMS comes with a different set of features and capabilities.
For an LMS to get the title of LMS, it needs to have the following three basic features:
On top of these, there are also advanced LMS features that are considered to be game-changers. These are the following:
While in the old days, it would have been impossible for an LMS to author, create, and sell learning content and activities and keep your content secure, some online learning platforms, including LearnWorlds allow you to do so.
Your professional looking Academy in a few clicks
Start FREE Trial
So, an LMS’s capabilities largely depend on whether or not it comes with such important features. Some LMSs can manage and deliver training content, while others can help you create and sell training.
What to Pay Attention to When Choosing an LMS?
If you are searching for an LMS solution, ensure you know what you are looking for regarding features, capabilities, and support and have a rough estimate of how much you are willing to invest in it. This should help you align the LMS vendor’s strengths with your training objectives and budget.
How much does a learning management system cost?
While there are many different pricing models, the price of an LMS may range depending on the type of LMS you choose and how many seats you need. The pricing is important because it determines an expense you set for yourself – your course business or on behalf of the organization you work for or represent.
How to choose a learning management system?
The first step is deciding what type of LMS you need. Should it be cloud-based or desktop-based? Currently, the cloud-based LMS is the most popular choice.
That’s because of the following:
These elements show that a cloud LMS is more cost-effective than a desktop one.
Also, make sure you further distinguish your options. For example, are you looking for a corporate LMS or academic LMS? What are your prerequisites and what are your needs?
Look carefully into the features it offers and its capabilities and match them to your own needs, in the same way you’d when buying a smartphone or laptop.
Finally, make sure you try out free demos and trials.
Your professional looking Academy in a few clicks
Start FREE Trial
What are some examples of learning management systems?
Because of their prevailing features and capabilities, some LMSs are better suited for academic, corporate, or enterprise LMSs.
Check out some examples for each.
Examples of academic LMS:
Examples of corporate LMS:
*As seen on the G2 list of Corporate LMS.
Examples of enterprise LMS:
*As seen on the eLearning Industry list of top Extended Enterprise LMS.
Top Online Learning Platforms:
*As seen on the G2 ratings on user satisfaction.
Take these LMS examples as an indication of the wealth of options available, but make sure you choose the one best suited to your needs.
Looking for the Best LMS for Your Business?
An LMS is an important component of online learning. As you can see, it is much more than just an e-learning platform for creating and delivering online education.
As education moves from traditional learning, online learning becomes part of a larger knowledge-based society. This rising trend encourages new businesses, coaches, and trainers to search for cost-effective solutions that improve productivity, provide effective training, and ensure performance.
So, why not use an LMS that can do all of that?
Start your journey with a top-notch LMS platform like LearnWorlds. Try it for free with a 30-day trial!
Your professional looking Academy in a few clicks
Start FREE Trial
The post What is an LMS (Learning Management System)? appeared first on LearnWorlds.

 : managing the role of academy staff e.g. the instructor, teacher, tutor, or manager (see user custom roles).
: managing the role of academy staff e.g. the instructor, teacher, tutor, or manager (see user custom roles). : keeping important information such as training resources safe and distributing content to those eligible to access it.
: keeping important information such as training resources safe and distributing content to those eligible to access it. : tracking and measuring each learner’s progress and performance.
: tracking and measuring each learner’s progress and performance. : Any LMS can also be equipped to create and manage course materials and learning content.
: Any LMS can also be equipped to create and manage course materials and learning content. : Gamification features include progress bar points, flashcards, badges/achievements, and actual games that are important for boosting learner engagement. LMSs that offer gamification have an added advantage over others.
: Gamification features include progress bar points, flashcards, badges/achievements, and actual games that are important for boosting learner engagement. LMSs that offer gamification have an added advantage over others. : With this feature, you can generate insightful data on who and how is using the system, looking into key training metrics like learner progress and course completion rates.
: With this feature, you can generate insightful data on who and how is using the system, looking into key training metrics like learner progress and course completion rates. : The ability to communicate in a social environment and exchange ideas and opinions is essential in learning. LMSs that offer social learning features like a dedicated learning community, discussion forums, and instant messaging are more advanced than others.
: The ability to communicate in a social environment and exchange ideas and opinions is essential in learning. LMSs that offer social learning features like a dedicated learning community, discussion forums, and instant messaging are more advanced than others. : Support has a huge role to play in an LMS. If it is inadequate or not there when you need it, you won’t be able to carry out your tasks effectively or use the software to its fullest potential.
: Support has a huge role to play in an LMS. If it is inadequate or not there when you need it, you won’t be able to carry out your tasks effectively or use the software to its fullest potential. : A key feature for virtual classroom-based classes especially for schools or academic institutions.
: A key feature for virtual classroom-based classes especially for schools or academic institutions. : The ability to offer learning on the go via a mobile app where learners can access training courses 24/7.
: The ability to offer learning on the go via a mobile app where learners can access training courses 24/7. : A friendly and easy-to-use user interface creates a positive user experience and is important for non-tech-savvy learners and users new to using eLearning technology.
: A friendly and easy-to-use user interface creates a positive user experience and is important for non-tech-savvy learners and users new to using eLearning technology. : Offering certificates is a must-have feature for learners who want to get certified in their career field and companies that want to provide such an opportunity to their employees.
: Offering certificates is a must-have feature for learners who want to get certified in their career field and companies that want to provide such an opportunity to their employees. : Not every LMS offers an e-commerce option allowing users to transact and sell digital products.
: Not every LMS offers an e-commerce option allowing users to transact and sell digital products. : An LMS should be able to integrate with third-party tools that allow data to roam freely and synchronized, offering more automation in terms of productivity, monetization, administration, and e-commerce.
: An LMS should be able to integrate with third-party tools that allow data to roam freely and synchronized, offering more automation in terms of productivity, monetization, administration, and e-commerce. : The ability to offer multi-language support that suits the needs of people based outside the LMS vendor’s origin country.
: The ability to offer multi-language support that suits the needs of people based outside the LMS vendor’s origin country. : The white labeling option allows you to remove the LMS vendor’s logo and add your own on your website host address URL and your homepage. A truly white-label option though gives you much more than the majority of LMSs can.
: The white labeling option allows you to remove the LMS vendor’s logo and add your own on your website host address URL and your homepage. A truly white-label option though gives you much more than the majority of LMSs can. : An LMS must be able to provide you with intellectual property protection that helps to secure your content, user information, and other sensitive data, but not every LMS can offer it.
: An LMS must be able to provide you with intellectual property protection that helps to secure your content, user information, and other sensitive data, but not every LMS can offer it.